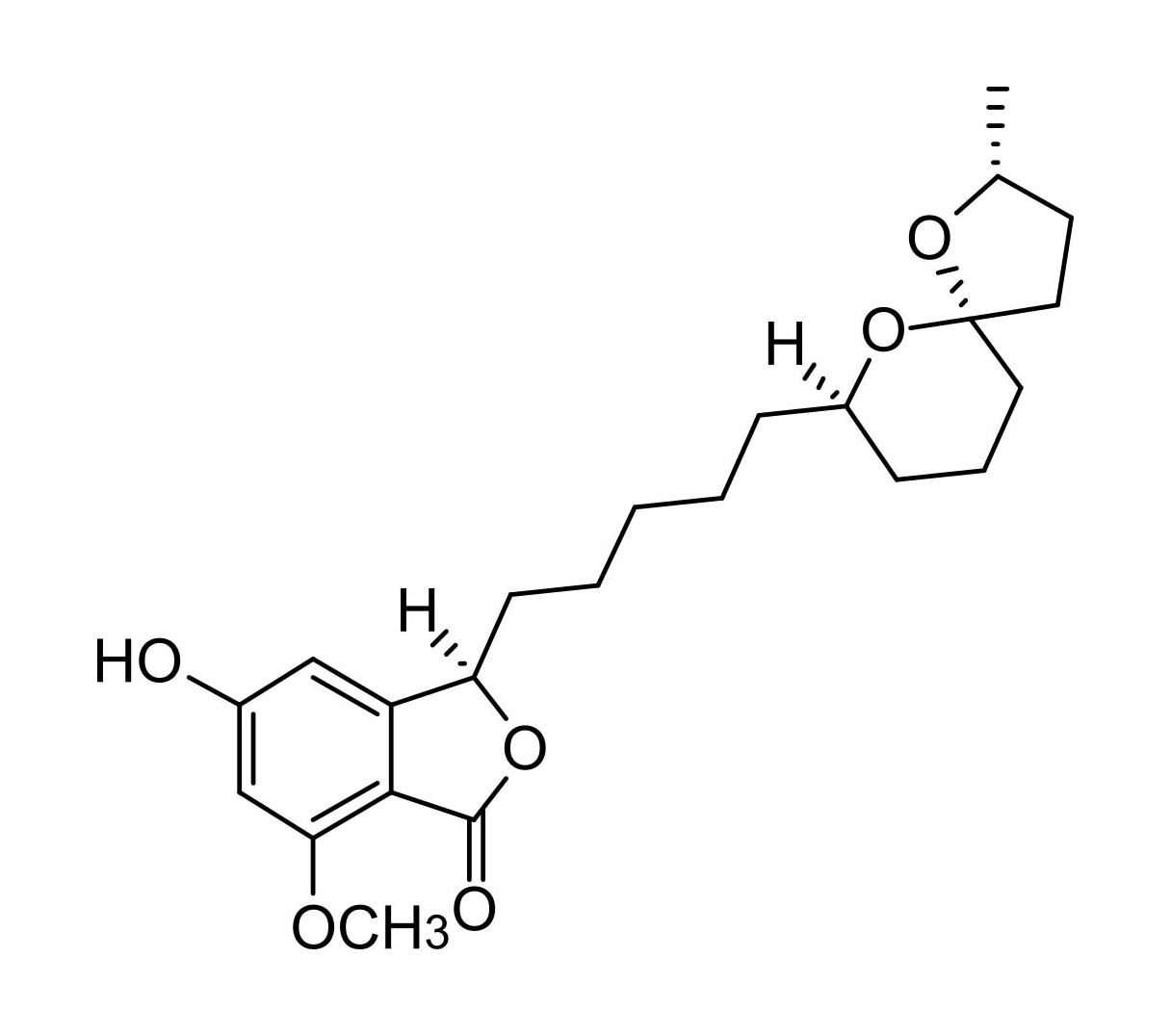
Spirolaxine
Application Notes
Spirolaxine is the major metabolite isolated from the white wood rot fungus, Sporotrichum laxum, reported by Arnone and co-workers in 1990. The absolute stereochemistry of spirolaxine was solved by researchers at CNR-ICRM, Italy in 2005. Spirolaxine follows a common biosynthetic route to phanerosporic acid but undergoes a series of hydroxylation, cyclisation and methylation steps. Spirolaxine is a potent antibacterial, specifically against Helicobacter pylori.
References
- Secondary mold metabolites. Part 28. Spirolaxine and sporotricale: two long-chain phthalides produced by Sporotrichum laxum. Arnone A. et al., Phytochem. 1990, 29, 613.
- Absolute configuration of the fungal metabolite spirolaxine. Bava A. et al., Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 11, 2292.
- Three new resorcylic acid derivatives from Sporotrichum laxum. Wang S. et al., Bioorg. & Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 5806.