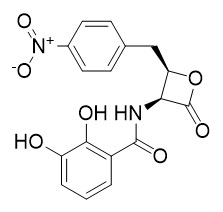
Obafluorin
Application Notes
Obafluorin is a β-lactone antibiotic produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens discovered by researchers at the Squibb Institute in 1984. Obafluorin is weakly active against Gram positive and Gram negative organisms, with a zone of inhibition against S. aureus of 7.4 – 8.7 mm, E. coli of 10.5 – 13.5 mm, E. cloacae of 9.3 mm, P. rettgeri of 7.7 mm and P. aeruginosa of 9.1mm at 10 µg/mL. Obafluorin is susceptible to hydrolysis by β-lactamases. Biosynthetically, obafluorin is catalysed by a rare non-ribosomal peptide synthetase.
References
- Obafluorin, a novel β-lactone produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Taxonomy, fermentation and biological properties. Well J.S. et al. J Antibiot 1984, 37, 802.
- The structural basis of N-acyl-α-amino-β-lactone formation catalyzed by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase. Kreitler D.F. Nature Comm 2019, 10, 1.