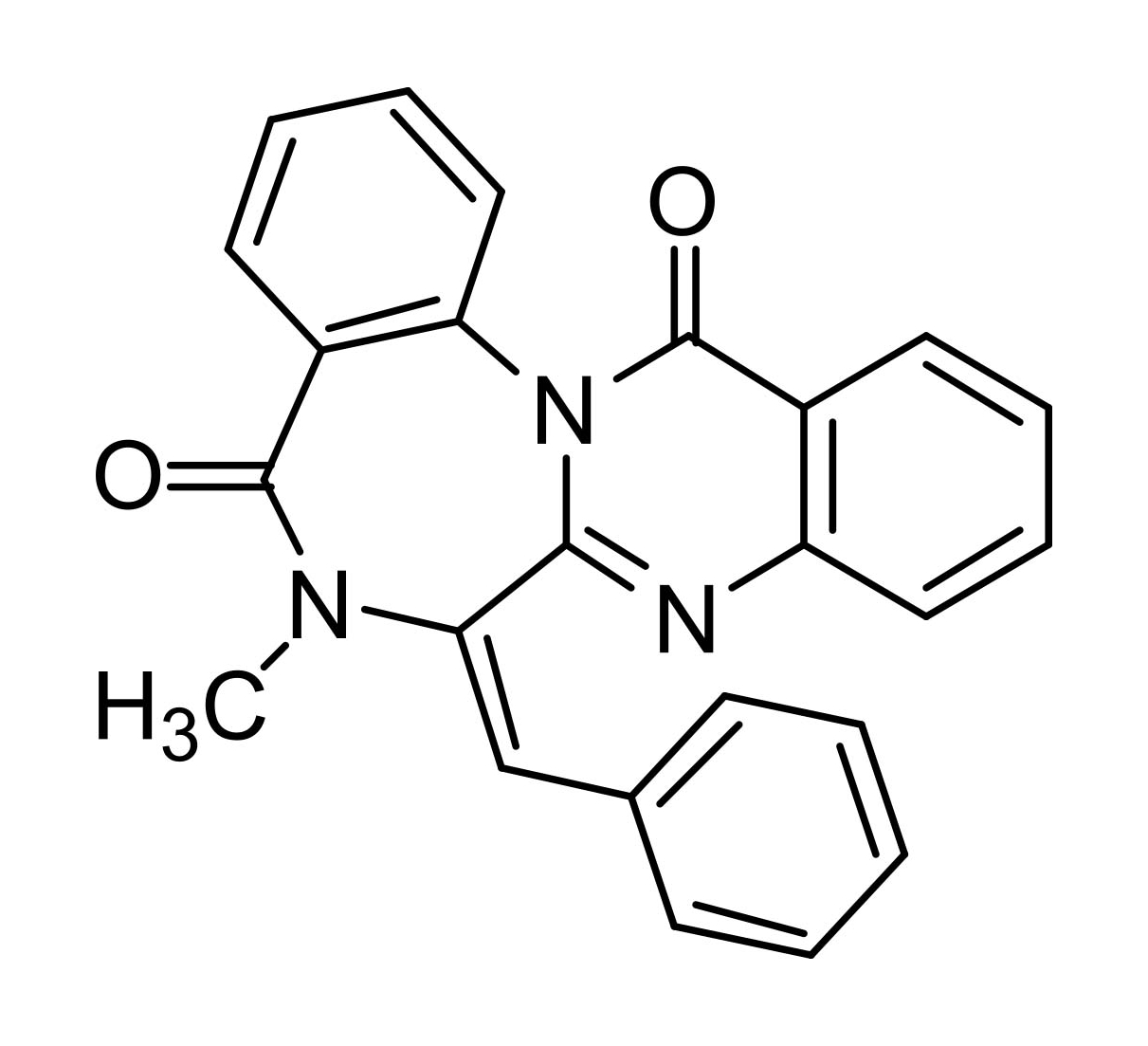
Benzomalvin B
Application Notes
Benzomalvin B was first isolated as a weakly active inhibitor of substance P from mammalian neurokinin NK1 receptors by researchers at Sterling Winthrop Pharmaceuticals (now Sanofi Aventis) in 1994. The core benzodiazepine structure of benzomalvin B is formed biosynthetically by the condensation of two molecules of anthranilic acid and phenylalanine. Benzomalvin B is related to the asperlicins, potent and selective antagonists of peripheral cholecystokinin receptors. Lack of availability has hampered further exploration of the pharmacology of benzomalvin B.
References
- Benzomalvins, new substance P inhibitors from a Penicillium sp. Sun H.H. et al., J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 515.
- The first total synthesis of (-)-benzomalvin A and benzomalvin B via the intramolecular aza-Wittig reactions. Sugimori T. et al., Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 7997.
- Asperlicin, a novel non-peptidal cholecystokinin antagonist from Aspergillus alliaceus. Fermentation, isolation and biological properties. Goetz M.A. et al., J. Antibiot. 1985, 38, 1633.