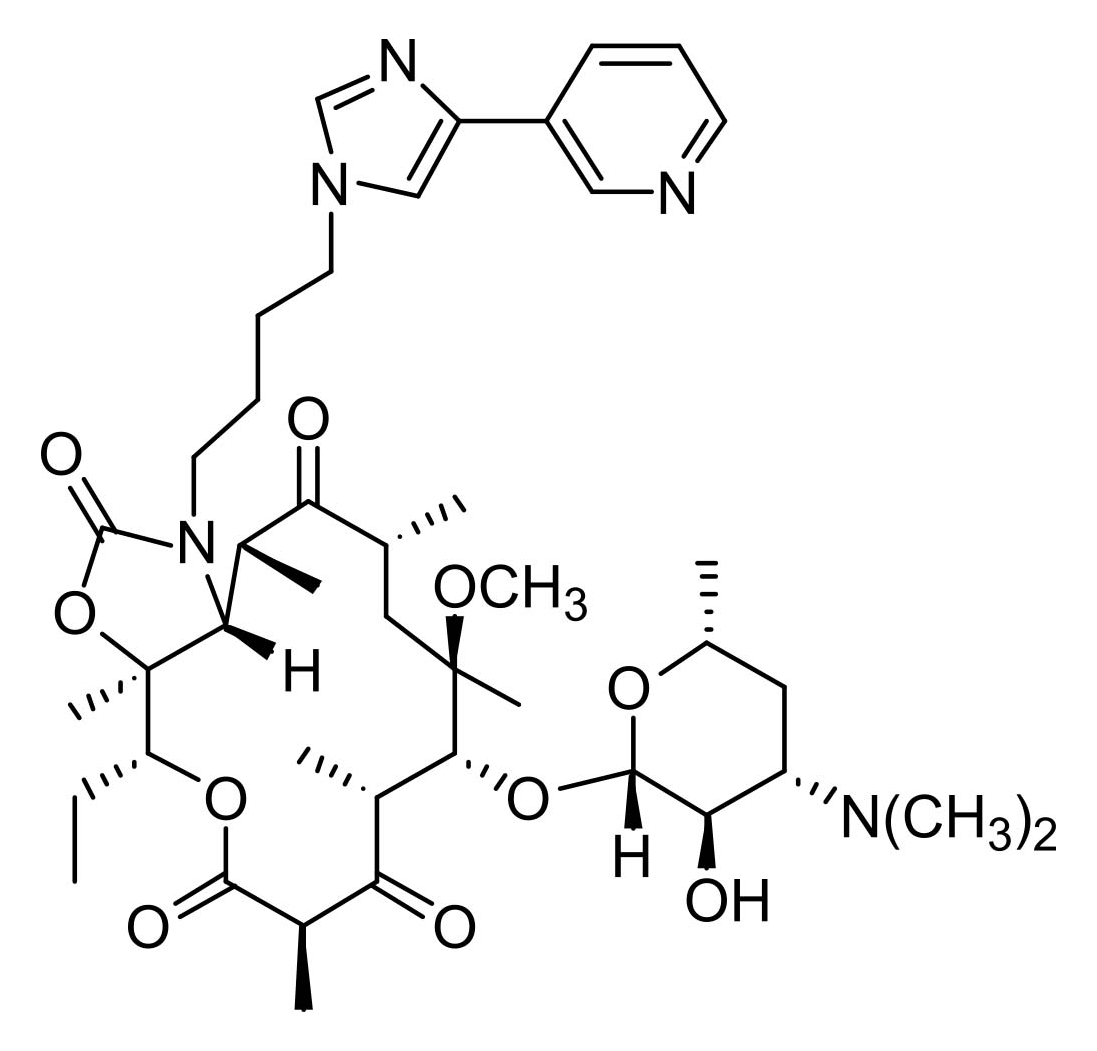
Telithromycin
Application Notes
Telithromycin represents the first member of the current generation of erythromycin descendants, belonging to the ketolide class. The ketolides are characterised by the hydrolysis of the cladinose sugar and subsequent oxidation of the alcohol to a ketone. Telithromycin is acid stabile and has good activity against erythromycin-resistant S. aureus, and improved pharmacokinetics.
References
- Synthesis and antibacterial activity of HMR 3647, a new ketolide highly potent against erythromycin–resistant and susceptible pathogens. Denis A. et al., Biorg. Med. Chem. Letter 1999, 9, 3075.
- In vitro activities of two ketolides HMR 3647 and HMR 3004 against gram-positive bacteria. Saez-Nieto J.A. & Vazquez C.L. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 930.
- Inhibition of translation and 50S ribosomal subunit formation in S. aureus all by 11 different ketolide antibiotics. Champney W.S. & Tober C.L. Curr. Microbiol. 1998, 37, 418.