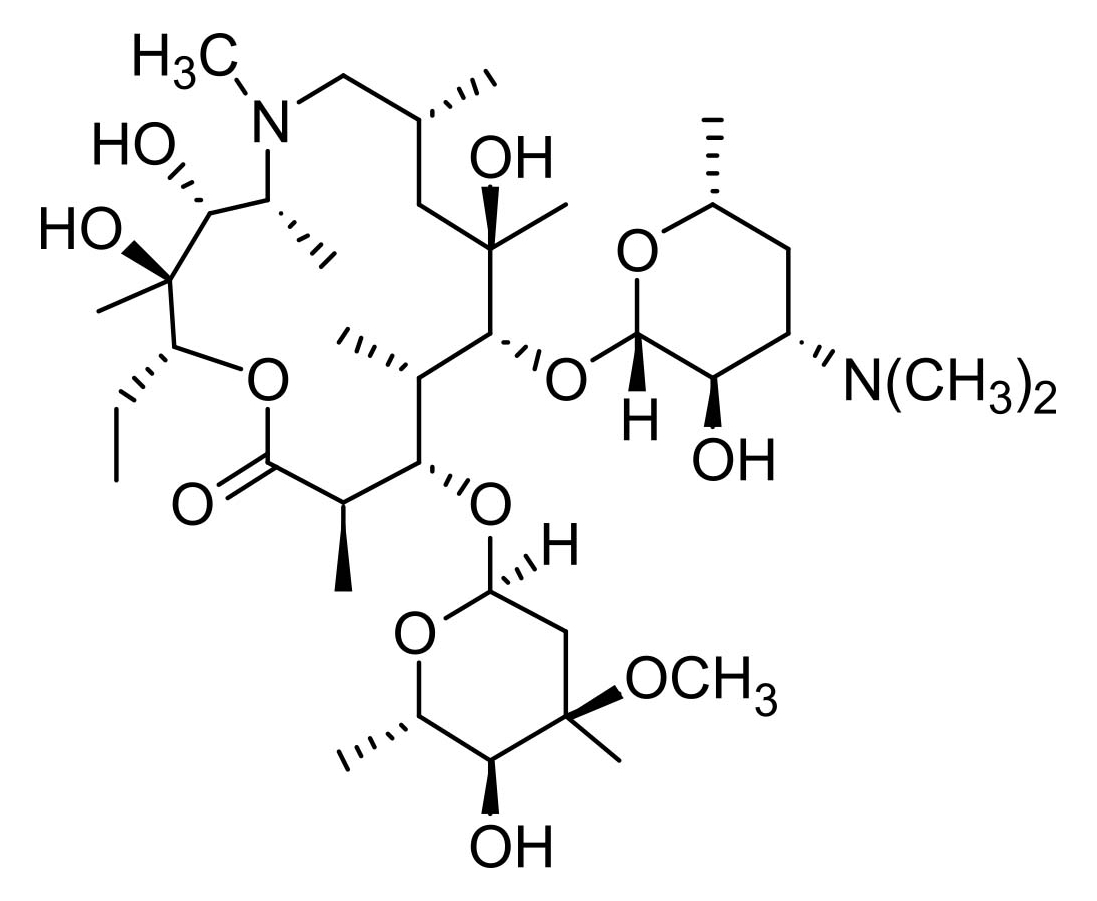
Azithromycin
Application Notes
Azithromycin is a semi-synthetic, ring-expanded erythromycin produced by a Beckmann rearrangement of erythromycin oxime and reduction to the imine ether, followed by reductive methylation. Azithromycin was the first of the azalides and was designed to improve the stability and biological half-life of erythromycin A, as well as improve activity against Gram negative bacteria. Since its discovery in 1980 by Djokic and co-workers, azithromycin has enjoyed considerable therapeutic success.
References
- 11-Aza-10-deoxo-10-dihydroerythromycin A and derivatives thereof as well as a process for their preparation. Kobrehel G. et al., 1982, U.S. Patent 4,328,334.
- Erythromycin series. XII Antibacterial in vitro evaluation of 10-dihydro-10-deoxo-11-azaerythromycin A: Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of its acyl derivatives. Djokic S. et al., J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 1006.